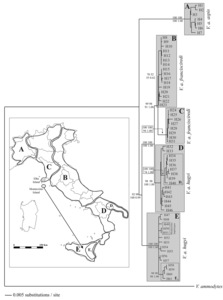
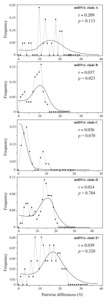
Barbanera, Filippo and Zuffi, Marco A.L. and Guerrini, Monica and Gentilli, Augusto and Tofanelli, Sergio and Fasola, Mauro and Dini, Fernando (2009) Molecular phylogeography of the asp viper Vipera aspis (Linnaeus, 1758) in Italy: evidence for introgressive hybridization and mitochondrial DNA capture. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 52/200 (1). pp. 103-114. ISSN 1055-7903
| PDF Download (189Kb) | Preview | |
![[img]](http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/598/2.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig._1.jpg)
| Other Download (167Kb) | Preview | |
![[img]](http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/598/3.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig._2.jpg)
| Other Download (436Kb) | Preview | |
![[img]](http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/598/4.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig._3.jpg)
| Other Download (271Kb) | Preview | |
![[img]](http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/598/5.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig._4.jpg)
| Other Download (184Kb) | Preview | |
![[img]](http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/598/6.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig._5.jpg)
| Other Download (150Kb) | Preview | |
![[img]](http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/598/7.hassmallThumbnailVersion/Fig._1_ESM.jpg)
| Other Download (78Kb) | Preview |
Abstract
SUMMARY Owing to its temperature dependence and low vagility, the asp viper (Vipera aspis) is an interesting model species to study the effects of Pleistocene climatic fluctuations on vertebrate genomes. We genotyped 102 specimens from the whole Italian distribution range at three mitochondrial DNA regions (2278 characters, total) and six microsatellite DNA loci (Short Tandem Repeats, STR). The molecular phylogeny was constructed according to Bayesian, Neighbour-Joining, Maximum Parsimony and Maximum Likelihood procedures. All methods grouped individuals of the three morphological subspecies (V. a. aspis, V. a. francisciredi, V. a. hugyi) into five different haploclades. Specimens assigned to hugyi clustered in two highly differentiated clades, one being sister group to the complex comprising the second clade of hugyi (i.e., a paraphyletic status), plus two clades of francisciredi. The Bayesian clustering of the STR variability disclosed only two groups, the first including aspis and francisciredi, the second all hugyi. Introgressive hybridization and capture of francisciredi-like lineages in the hugyi mitochondrial genome were suggested to explain the discordance between mitochondrial and nuclear data. The phylogeographic pattern was compatible with population contractions in three glacial refuges. Plausibility of derived hypothesis was checked using coalescence simulations as post hoc tests. Long-term drift and serial founder-effects, rather than selection, appeared the main factors affecting the genetic make-up of the Italian asp viper.
| Item Type: | Article |
|---|---|
| Uncontrolled Keywords: | V. a. aspis, V. a. francisciredi, V. a. hugyi, mitochondrial-nuclear DNA discordance, Pleistocene glacial refuges |
| Subjects: | Area05 - Scienze biologiche > BIO/05 - Zoologia Area05 - Scienze biologiche > BIO/18 - Genetica |
| Divisions: | Dipartimenti (until 2012) > DIPARTIMENTO DI BIOLOGIA |
| Depositing User: | Dr. Filippo Barbanera |
| Date Deposited: | 29 Jun 2009 |
| Last Modified: | 20 Dec 2010 11:52 |
| URI: | http://eprints.adm.unipi.it/id/eprint/598 |
Repository staff only actions
| View Item |